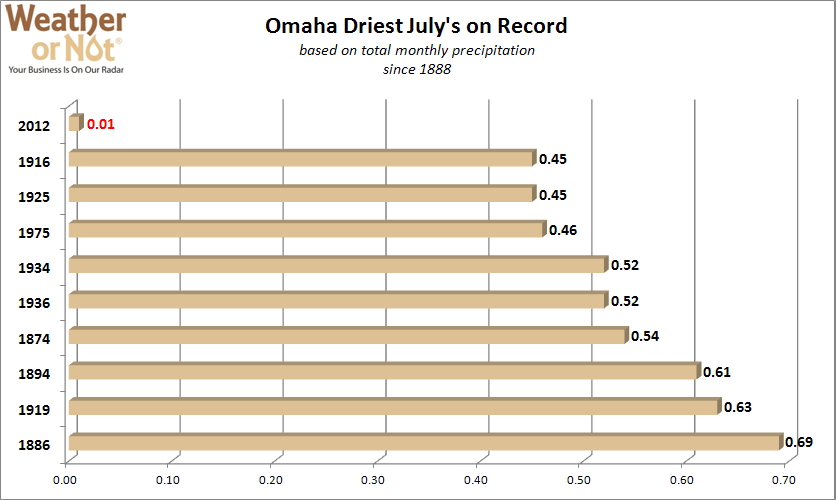
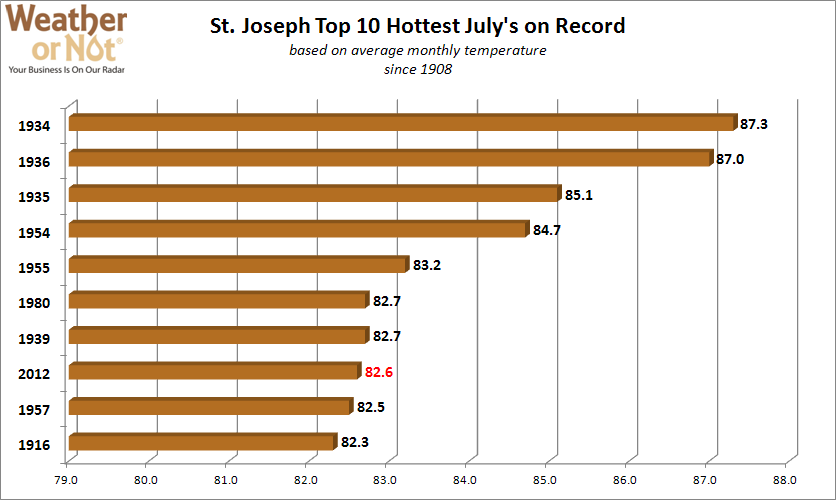
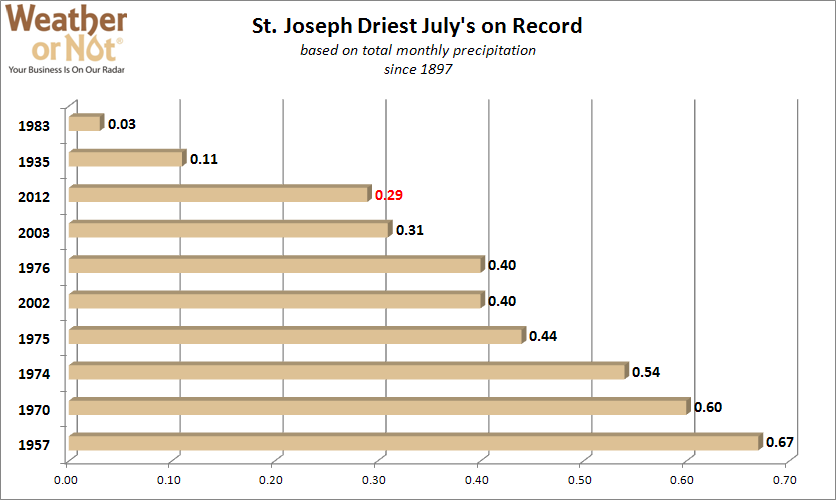
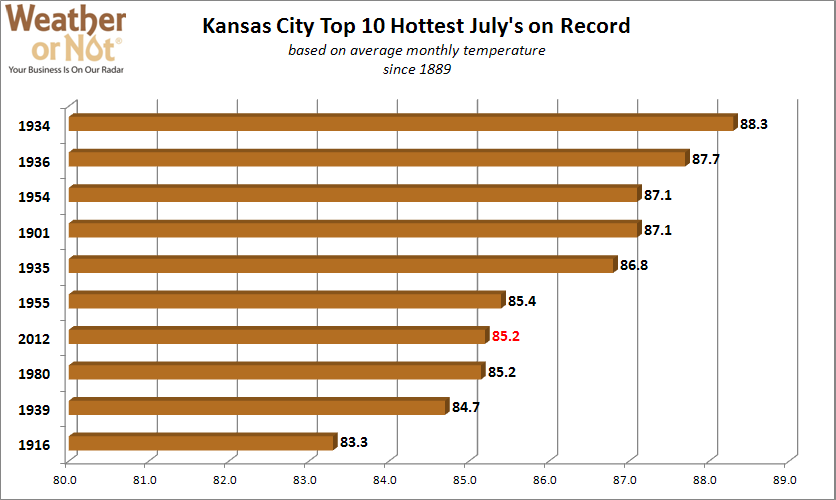
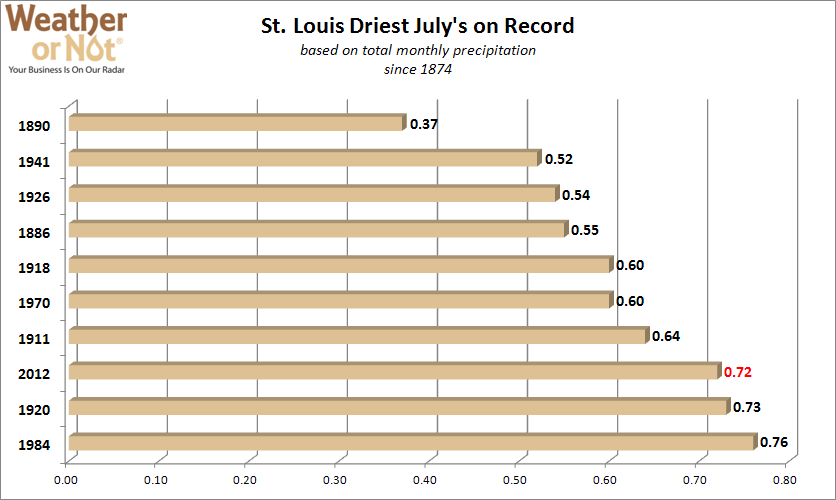
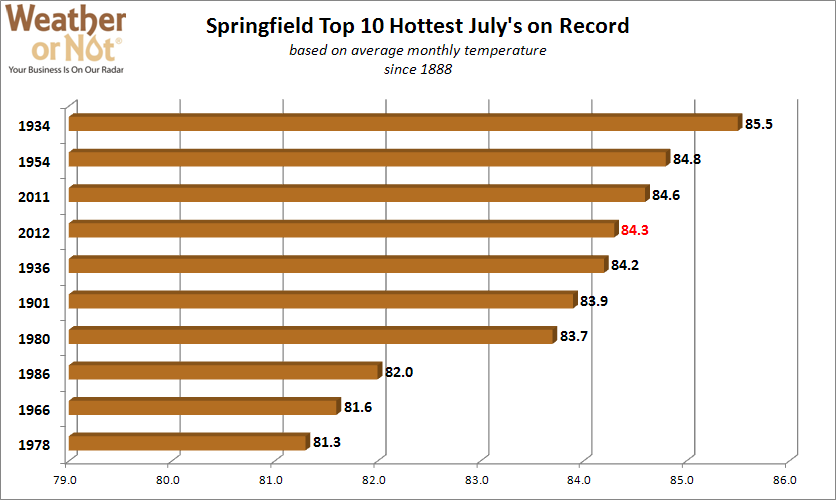
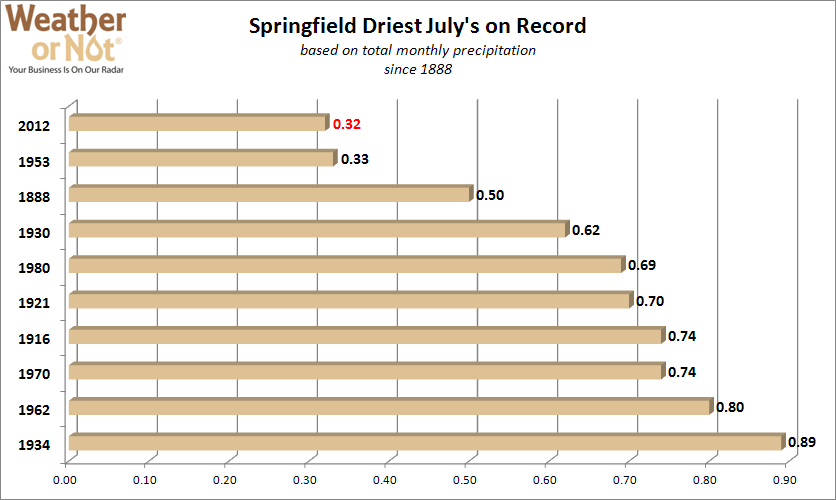
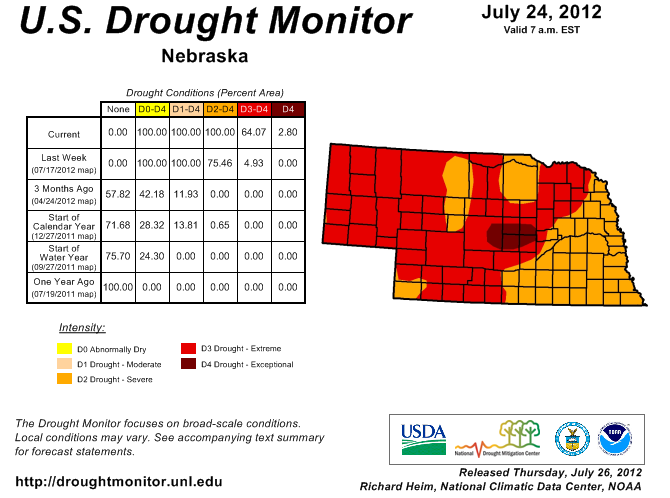
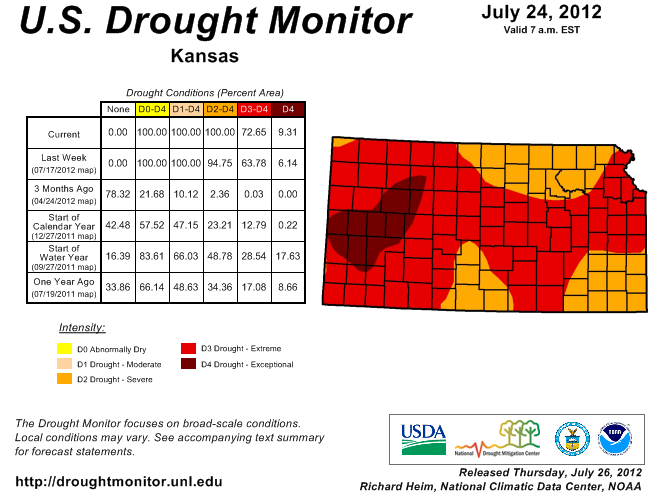
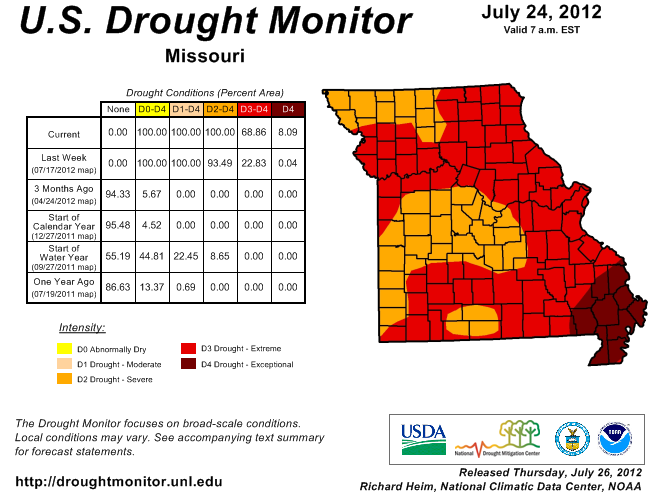
August 20, 2012
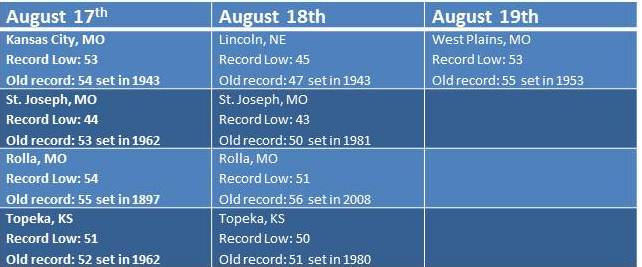
Low dewpoints, clear skies and light winds were the perfect recipe for record low temperatures this weekend. Let’s take a look at how each of these factors contributed to some cool mornings…
START WITH – Low Dewpoints: The dewpoint is a measure of the amount of moisture in the atmosphere. When dewpoints climb above 60 degrees in the summer, the air feels warm and muggy. Warm dewpoints on a summer night also limit cooling. This is because as the air temperature gets close to the dewpoint, relative humidity increases and condensation occurs. The process of condensation releases heat into the air causing the temperature to level-off near the dewpoint. So when the dewpoint is lower, that “level-off” happens at a lower temperature. That was the case this weekend as dewpoints dropped into the 40s.
ADD IN – Clear Skies: Starry skies are needed for temperatures to fall close to the dewpoint. During the day pavement, buildings, vegetation and soil absorb heat from the sun. During the night, that heat gets released back toward space. When the nighttime sky is cloudy, those clouds act like a blanket at night, keeping temperatures warm. However, when the nighttime sky is clear, heat released from earth escapes into space causing temperatures to drop. Locations that saw record lows this weekend all had clear skies for a majority of the night.
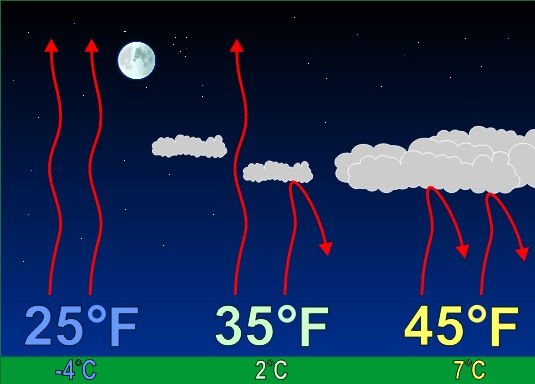
In winter, we welcome the cloudy blanket for warmth.
MIX WITH – Light Winds: Wind speed is the final factor in how low temperatures can fall. Since air normally cools from the ground up, the air closest to the ground is the coolest overnight. As you increase in elevation off the ground, the temperature normally gets warmer. If the wind is strong overnight, the cool air near the surface mixes with the warmer air above, which limits the potential for cooling. However, on a night with light winds, the air near the ground continues to cool with no influence from warm air above. Wind speeds were generally less than 5 mph this weekend.